 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
Caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis, pertussis or whooping cough leads to an infection in the respiratory system. It is more common in babies under the age of 6 months who have not received any vaccination and kids between 11 and 18 years of age whose immunity is no longer strong enough to prevent the infection.
When your child becomes infected, you will notice severe coughing spells with a "whooping" sound in the end. You can notice this sound when your child breathes in. There may also be some common cold symptoms that go way in a couple of week but severe coughing may continue for up to 3 months.
Yes, it can be very contagious and spread from person to person by sneezing or coughing. You may even become infected if you share bathing space with someone with infection. Studies show that a person with pertussis infects 12 people on average.
What you should bear in mind though is that the condition is most contagious during the first stage, which lasts about 1-2 weeks long. And it may remain contagious a month after the cough starts.
Now that you know the answer to your question, "Is whooping cough contagious?" you may also want to learn how to tell if someone is already infected. It usually takes 7-10 days for symptoms to appear after you have contracted the infection. The incubation period can sometimes be as long as 21 days. There may be different symptoms in babies, young children and adults.
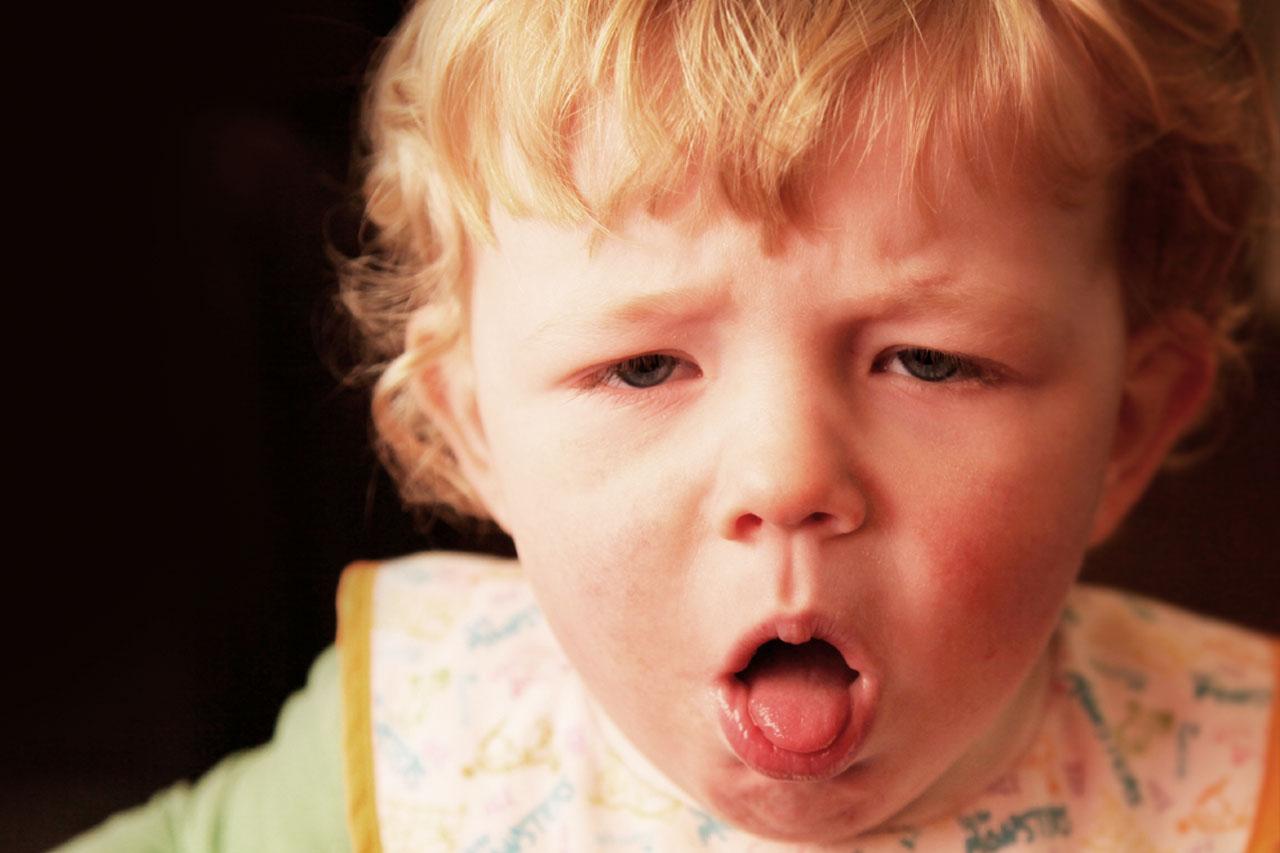 If your baby is under 6 months of age and become infected, they may not whoop at all. They may, however, stop breathing, get exhausted from coughing, or appear to have a cold. You may find it difficult to feed them because of coughing, which will result in loss of weight.
If your baby is under 6 months of age and become infected, they may not whoop at all. They may, however, stop breathing, get exhausted from coughing, or appear to have a cold. You may find it difficult to feed them because of coughing, which will result in loss of weight.
The illness may work in three stages in young children.
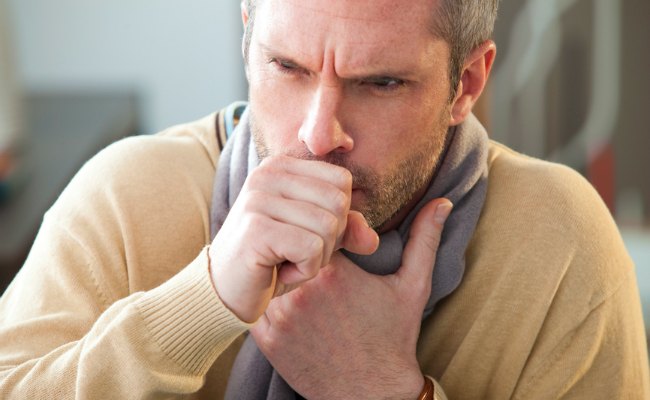 Just like young children, adults will also experience symptoms of common cold first. These symptoms may include tiredness, low-grade fever, runny nose, and a mild cough. Before long, the cough will become severe. Many people have severe coughing fits and they gasp for breath between fits. It is also common to vomit after coughing fits and feeling exhausted.
Just like young children, adults will also experience symptoms of common cold first. These symptoms may include tiredness, low-grade fever, runny nose, and a mild cough. Before long, the cough will become severe. Many people have severe coughing fits and they gasp for breath between fits. It is also common to vomit after coughing fits and feeling exhausted.
Is whooping cough contagious? Yes, it is. Can it be prevented? Yes, you can take steps to lower your risk for getting infected.
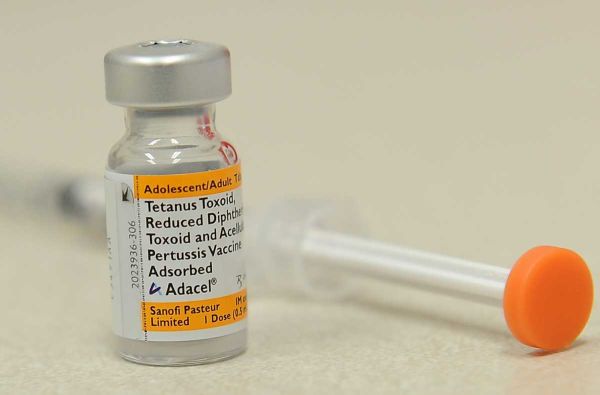 You should get the pertussis vaccine first and ensure that your children get it with vaccines for other serious diseases, including tetanus and diphtheria. It is important to start vaccination during infancy. Your child gets a series of five injections when they are 2 months old, 4 months old, 6 months old, 15-18 months old, and 4-6 years old.
You should get the pertussis vaccine first and ensure that your children get it with vaccines for other serious diseases, including tetanus and diphtheria. It is important to start vaccination during infancy. Your child gets a series of five injections when they are 2 months old, 4 months old, 6 months old, 15-18 months old, and 4-6 years old.
It is also important to go for booster shots at certain ages. For instance:
It is essential for people who work in settings where they are close to babies and infants to get the vaccine. It is important because whooping cough can cause life-threatening complications in babies.
 Antibiotics
AntibioticsWhile getting vaccinated is one way to prevent whooping cough, it sometimes becomes important to take antibiotics to ensure you do not spread the disease. You already know the answer to, "Is whooping cough contagious?" so you have to take antibiotics if you live with someone who has pertussis.
 It is important to practice good hygiene to ensure you do not spread the respiratory illnesses. Here are some steps to take:
It is important to practice good hygiene to ensure you do not spread the respiratory illnesses. Here are some steps to take: