 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
Barium test is a diagnostic measure to get images of the gastrointestinal tract. When regular X-ray images are taken, the gut does not show up very well on the image. For this reason, the patient is asked to take a barium meal which is a white liquid containing the chemical barium sulphate. This chemical outlines the upper gastrointestinal tract which includes the esophagus, stomach and small intestine. Since X-rays do not pass through the barium, the tract gets highlighted in the images. This test is also known as barium swallow sometimes.
When a person complains of chest pain, acid reflux or difficulty in swallowing, the doctor usually recommends barium meal test. It is also recommended when there is unexplained vomiting, abdominal pain, indigestion or presence of blood in stools. This happens when there is blood loss from the stomach or other part of the gastrointestinal tract. Barium meal can help in diagnosis of inflammation, ulcer or tumor of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum.
If you do not wish to have a barium meal, you can opt for a procedure called gastroscopy. In this procedure, a gastroscope is inserted through the mouth to check the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Gastroscope is narrow, flexible tube like instrument with camera to take the images. Another option is to undergo CT-scan which takes 3-dimensional images of the gut. Sometimes various diagnostic measures are required to get the final conclusion.
You will have to be on an empty stomach prior to having the barium meal, and thus do not have any food or drinks from the midnight before the test. All test centers provide different fasting instructions and will have to be followed accordingly. Smoking should also be avoided as it increases gastric secretions. Some doctors also ask patients to not take medications on the day of the test, especially antacids. Diabetics should also ask for any specific instructions pertaining to their condition.
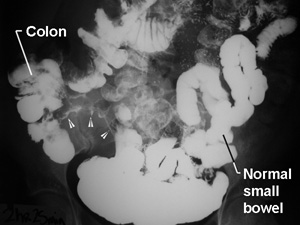 During a barium meal examination, the patient is given liquid barium to swallow, along with granules and citric acid mixture. The granules combine with citric acid and release carbon dioxide which causes distention of the gut. The distention caused by carbon dioxide should remain and hence the patient should avoid burping. Depending on the type of images required, the patient is asked to lie in different positions – standing, sleeping, etc. The X-ray machine takes images and the exact time when image is taken the patient needs to hold his breath. Once the images are satisfactory, the patient can leave.
During a barium meal examination, the patient is given liquid barium to swallow, along with granules and citric acid mixture. The granules combine with citric acid and release carbon dioxide which causes distention of the gut. The distention caused by carbon dioxide should remain and hence the patient should avoid burping. Depending on the type of images required, the patient is asked to lie in different positions – standing, sleeping, etc. The X-ray machine takes images and the exact time when image is taken the patient needs to hold his breath. Once the images are satisfactory, the patient can leave.
The X-ray images taken after the barium meal are examined by a radiologist in detail. A detailed report is prepared by the radiologist regarding the findings, which will then have to be discussed with your doctor on the follow up visit. The barium can cause constipation; hence the patient should consume fiber rich foods and drink plenty of liquids. The stools will be white for 2-3 days after the barium meal test. In case any other problems are experienced, doctor should be consulted.
There are some risks associated with barium meal test, which the radiologist can explain when you are going to have the test. The chances of risk occurring and the intensity of risk differs from person to person. The first risk is of X-ray exposure, which is always kept at minimum level. Pregnant women are generally not recommended to get X-rays as it can cause damage to unborn child.
A barium meal will cause temporary side effects like bloating for a short period. This is followed by constipation, for which mild laxative would be required. A muscle relaxant is given during the test, which may cause blurred vision and dryness in the mouth for some time. It can also cause difficulty in urination. Complications, if any, occur during or immediately after the procedure. For instance, an allergic reaction may happen and causes itching and difficulty in breathing. Radiographer should be informed immediately if this happens, who will administer anti-allergic medication.