 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
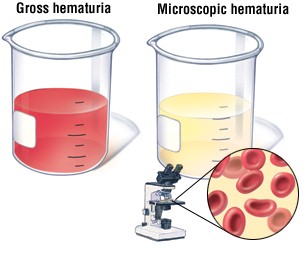
Blood in urine or hematuria, is not a good sign as it can be a symptom of a dangerous disease or disorder. Whenever you see blood in urine, it becomes necessary to ascertain its cause. Hematuria is of two main types: microscopic hematuria and gross hematuria. Microscopic hematuria is one in which the blood in urine cannot be seen without the use of a microscope and is discovered only after conducting a medical test. Gross hematuria on the other hand is one in which the urinary blood can be seen without the aid of a microscope.
Hematuria that results from strenuous exercise does not require any medical treatment and it will disappear in a few days. However, other disorders causing blood in urine may require extensive medical care depending on the severity of the disorder.
 There are many other symptoms that may be experienced by sufferers of urinary bleeding depending on the disorder that is causing it. The symptoms that might follow blood in urine include:
There are many other symptoms that may be experienced by sufferers of urinary bleeding depending on the disorder that is causing it. The symptoms that might follow blood in urine include:
Besides these common symptoms, there are other serious indications as well which include:
You must visit a doctor if you are having difficulty urinating or are suffering from pain in your kidneys or abdomen since it may be a symptom of microscopic hematuria. It is also essential to seek immediate medical care if you witness blood in your urine as it can be an indication of a serious medical problem. Failing to notice even a little quantity of urinary blood could be catastrophic.
Look for immediate medical assistance if you are unable to urinate or are witnessing blood clots in your urine. Visit a hospital right away if this urinary blood is followed by chills, fever, vomiting, nausea and abdominal, back or side pain.
The ramifications for neglecting urinary blood can be very severe. Your kidneys might fail if the hematuria is stemming from an infection that is not treated in time. There is also a chance that the cause of this blood is a cancer and if it is not diagnosed and treated in time, the cancer might metastasize and spread to other parts of the body.
Hematuria can result from a number of causes. There is a chance that the blood visible is stemming from a source other than your bladder or kidney. The blood that you are seeing might be coming from the bowel movement, vagina or ejaculation. The following are some of the causes of urinary bleeding.
|
Causes |
Description |
|
Infections |
Urinary tract and kidney infections can both cause hematuria. In both these infections, the bacteria get in the body through the urethra and target the bladder and the kidneys respectively. The symptom of urinary tract infections is pain felt when urinating while that of kidney infection is back and abdominal pain accompanied by high grade fever. |
|
Stone |
Kidney or bladder stones can cause both gross and microscopic hematuria and can cause unbearable pain for the patients. |
|
Prostate problem |
Enlargement of the prostate or a prostate infection can result in microscopic hematuria. The symptoms are urgency and pain felt when urinating. |
|
Kidney disease |
Kidney disease can occur due to a number of reasons and is of the most common causes of microscopic hematuria. |
|
Cancer |
Cancers of the kidney, prostate and bladder might cause urinary bleeding at an advanced stage. |
|
Inherited disorders |
Alport syndrome and sickle cell anemia which are both hereditary disorders can cause both gross and microscopic hematuria. |
|
Kidney injury |
Gross hematuria can be caused due to an injury or trauma suffered by the kidneys during an accident. |
|
Medication |
Constant use of drugs like heparin, cyclophosphamide, penicillin and aspirin can cause gross hematuria. |
|
Strenuous exercise |
Having an intense workout can sometimes cause gross hematuria due to dehydration. |
Treatment for blood in urine depends on its cause and is directed towards eliminating it. Once the treatment has been administered, the doctor is likely to check if the problem has been dealt with or not. If he still finds urinary bleeding then the doctor might refer you to an urologist or ask for additional tests to be performed on your urine.
For people whose underlying cause for urinary bleeding cannot be detected even after performing the necessary tests, the doctor might advise regular checkup and urine testing. The need for urine testing and monitoring of blood pressure becomes particularly necessary for people who are more than 50 years old, who are regular smokers or who have been exposed to hazardous chemicals as they are at an increased risk of developing bladder cancer.
It is impossible to stop the appearance of blood in urine. However, you can take precautionary steps to minimize the chances of contracting diseases that cause hematuria.