 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
Chronic prostatitis affects men and causes inflammation and pain in the prostate gland, which is located in the lower urinary tract directly underneath the bladder. This condition is most prevalent in men who are aged between 35 and 50. Left untreated, this condition can develop into serious urinary and sexual problems. Out of every 10 men, 1 or 2 will get chronic prostatitis some time in their life. Two million annual visits to the doctor are related to an inflamed prostate.
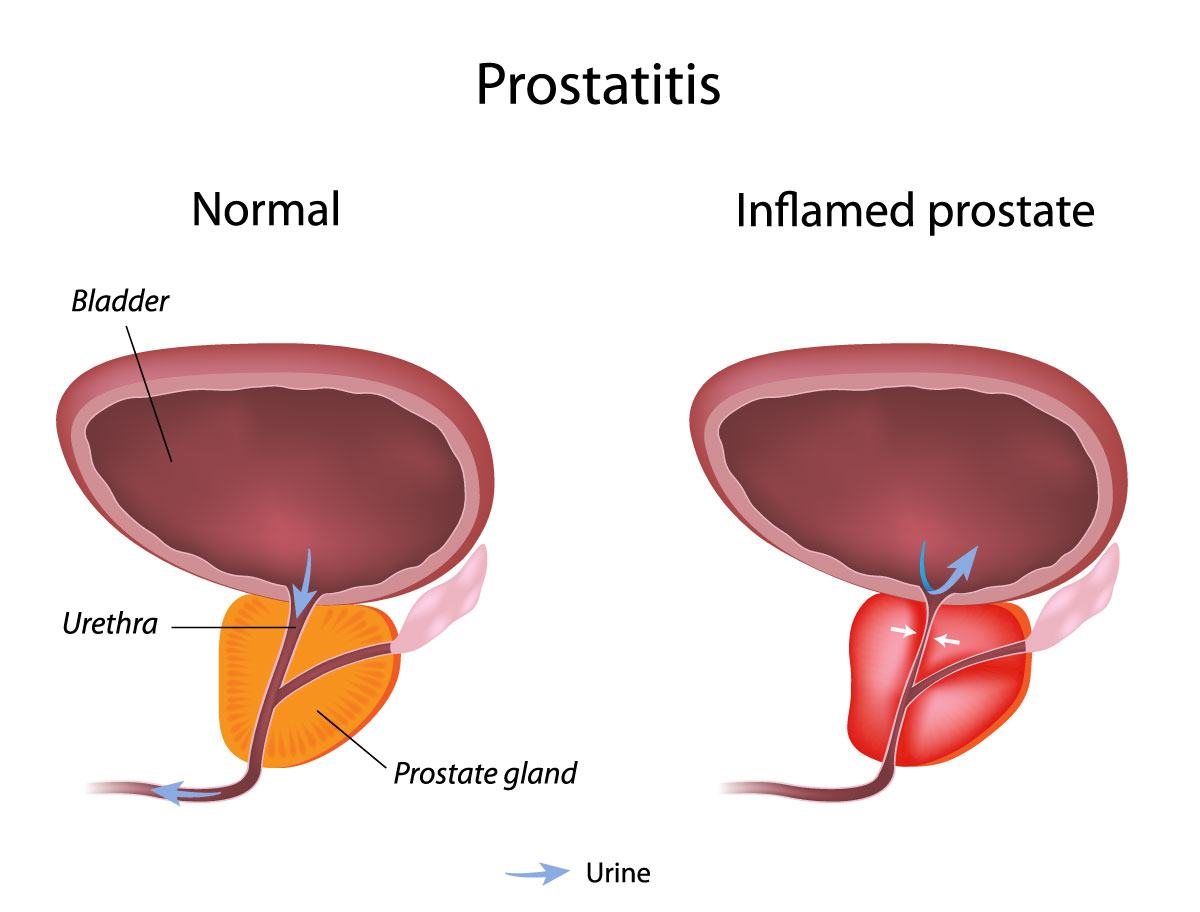 The term "prostatitis" refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland. It can either be chronic (persistent) or acute. On the other hand, it can be non-infective or infective.
The term "prostatitis" refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland. It can either be chronic (persistent) or acute. On the other hand, it can be non-infective or infective.
For you to be diagnosed with chronic prostatitis, you must have had the symptoms for 3 months or more. For acute prostatitis, the symptoms show up and disappear much faster. There are 2 major types:
This condition's symptoms normally vary in intensity from time to time. You will mostly feel discomfort and pain around the anus, at penis' base, in your lower back and/or just above the pubic bone. The pain can spread to the testes and penis. You might also feel some discomfort when you are passing stool. In addition, you might have symptoms similar to a urine infection. These symptoms include passing urine often, pain when urinating or a pressing urge to urinate.
Acute bacterial prostatitis has similar symptoms, but men with chronic prostatitis are usually less sickly compared those suffering from acute bacterial prostatitis. They are not likely to experience pains, aches and high fever.
When antibiotics are administered, symptoms of this condition normally reduce. Nevertheless, if the antibiotics don’t clear the infected prostate, it is more likely that the illness will flare-up again. Before the infection comes back, you are likely to have mild urine infection symptoms like frequently passing urine and mild pain.
In this case, symptoms have been observed for 3 months in the past 6 months. These symptoms are:
If you feel pelvic pain, painful or difficult urination and painful ejaculation (orgasm), it is wise to pay your doctor a visit. Some types of prostatitis can cause other health problems or worsening infections if left untreated.
This is a form of infective prostatitis. It is mainly caused by a persistent (chronic) infection in the prostate gland. A man who has this condition will keep having urine infections over and over. The type of bacteria that causes urine infections is also responsible for this condition. The infection can be harbored in the prostate gland making the infection recur. It is, however, important to note that prostatitis isn't sexually transmitted.
The cause of this type of prostatitis is unknown. However, there are many theories that try to explain its cause. They include nerve problems affecting the prostate, infection of the gland by an unidentified germ, an autoimmune problem of the prostate (the antibodies that are meant to be fighting diseases are fighting the prostrate instead), and inflammation as a result of urine moving back into the prostrate when passing urine.Different people respond differently to anti-inflammatory painkillers and antibiotics. For this reason, doctors prefer calling this condition chronic pelvic pain syndrome to disassociate it from the prostate gland being the root of the problem.
Risk factors for this condition include:
The possible treatments include:
Possible treatments include:
Some of the home remedies that can reduce the symptoms of prostatitis include: