 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
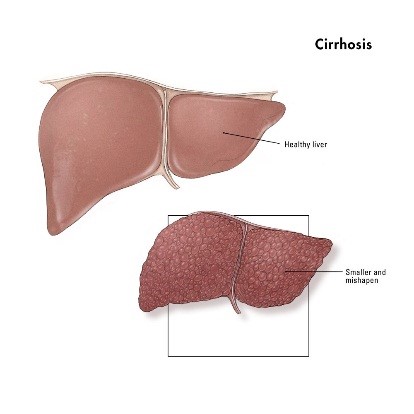
Cirrhosis of the liver is a serious complication of chronic liver disease, which leads to abnormal liver structure and function. Many liver diseases cause injury and kill the liver cells, leading to scar tissue formation. Surviving liver cells multiply, in their attempt to replace the dead cells, resulting in clusters or regenerative nodules within the scarred liver. Causes of liver cirrhosis include chemicals, toxic metals, viruses, and autoimmune disease.
 Symptoms of liver cirrhosis usually do not appear until the late stages of the disease. They occur when the liver fails to detoxify the blood, to produce blood-clotting proteins, and to aid in the metabolism of fat. These symptoms include:
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis usually do not appear until the late stages of the disease. They occur when the liver fails to detoxify the blood, to produce blood-clotting proteins, and to aid in the metabolism of fat. These symptoms include:
Serious symptoms of cirrhosis include:
Call your doctor if your symptoms do not improve in one or two days, or if you have these symptoms:
Go to the emergency department if you cannot reach your doctor when you have:
Liver cirrhosis is caused by the formation of scar tissue in the liver after damage has occurred over the years. The liver tries to repair itself every time it is damaged, and as scar tissues develop, liver function declines, until it no longer works well.
A wide range of conditions can cause damage to the liver, leading to cirrhosis. Some of these are inherited conditions, such as:
Others liver conditions develop later in life, including:
Some people develop cryptogenic cirrhosis, a condition where doctors cannot find a cause for liver disease.
There is no permanent cure for liver cirrhosis, but there are treatments that can delay or stop its progress, reduce damage to the liver cells, and minimize its complications.
The treatment may depend on the cause of the cirrhosis:
Medications to control symptoms of the disease include diuretics (water pills) to reduce fluid retention. A reduction of salt in the diet is also important. Diet changes and medications can help improve altered mental functions. Laxatives may be given to increase the removal of toxins from the intestines.
People with severely damaged livers may need liver transplantation to survive.
Cirrhosis cannot be reversed. However, it is important to prevent or reduce further damage to the liver by:
Watch the video to have a general idea on cirrhosis of the liver: