 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
Fungal infections are one of the most unpleasant skin diseases. They are caused by microorganisms called fungi, which live in our environment. These fungi can be found in the air, water, soil, plants and even people. Indeed, human body hosts some types of fungi which are basically harmless. But sometimes, due to certain factors, they grow and multiply in the body to such an extent as to cause infection. Some of them tend to attack a kind of protein in the body, called keratin, which is found in the outer layer of the skin and also in the hair and nails. These fungi are the main culprits for fungal skin infections.
Fungal infections can appear anywhere in the body, including feet, scalp, nails and groin. These conditions can generally be cured by ointments or pills. However, they can cause serious complications, especially if the body’s immune system is week. Here are the most common skin infections:
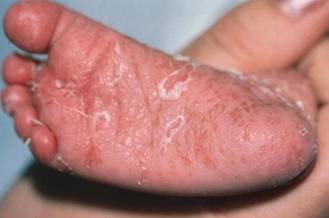
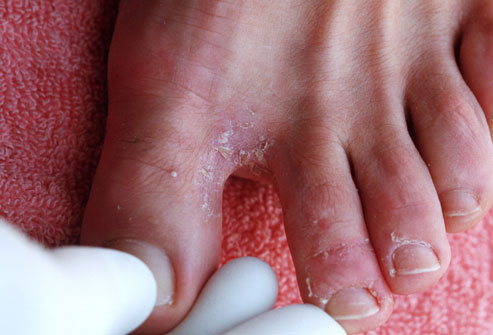 Athlete’s Foot, also called tinea pedis, is a fungal infection which affects feet. It usually causes redness, itching, burning, peeling, sometimes even blisters and sores. This fungus thrives in warm, moist environment, such as shoes, socks, swimming pools, etc. Athlete’s foot is caused by an even smaller micro-fungus which is met on the dead tissue of hair, toenails and outer skin layers.
Athlete’s Foot, also called tinea pedis, is a fungal infection which affects feet. It usually causes redness, itching, burning, peeling, sometimes even blisters and sores. This fungus thrives in warm, moist environment, such as shoes, socks, swimming pools, etc. Athlete’s foot is caused by an even smaller micro-fungus which is met on the dead tissue of hair, toenails and outer skin layers.
Symptoms: peeling, cracking or scaling of the foot, redness, blisters, softening and increased vulnerability of the skin, itching and burning
Treatment: Athlete’s foot is treated by antifungal medication, which is administered directly on the affected area of the skin. More serious cases may require oral medication – pills or other drugs taken by mouth.
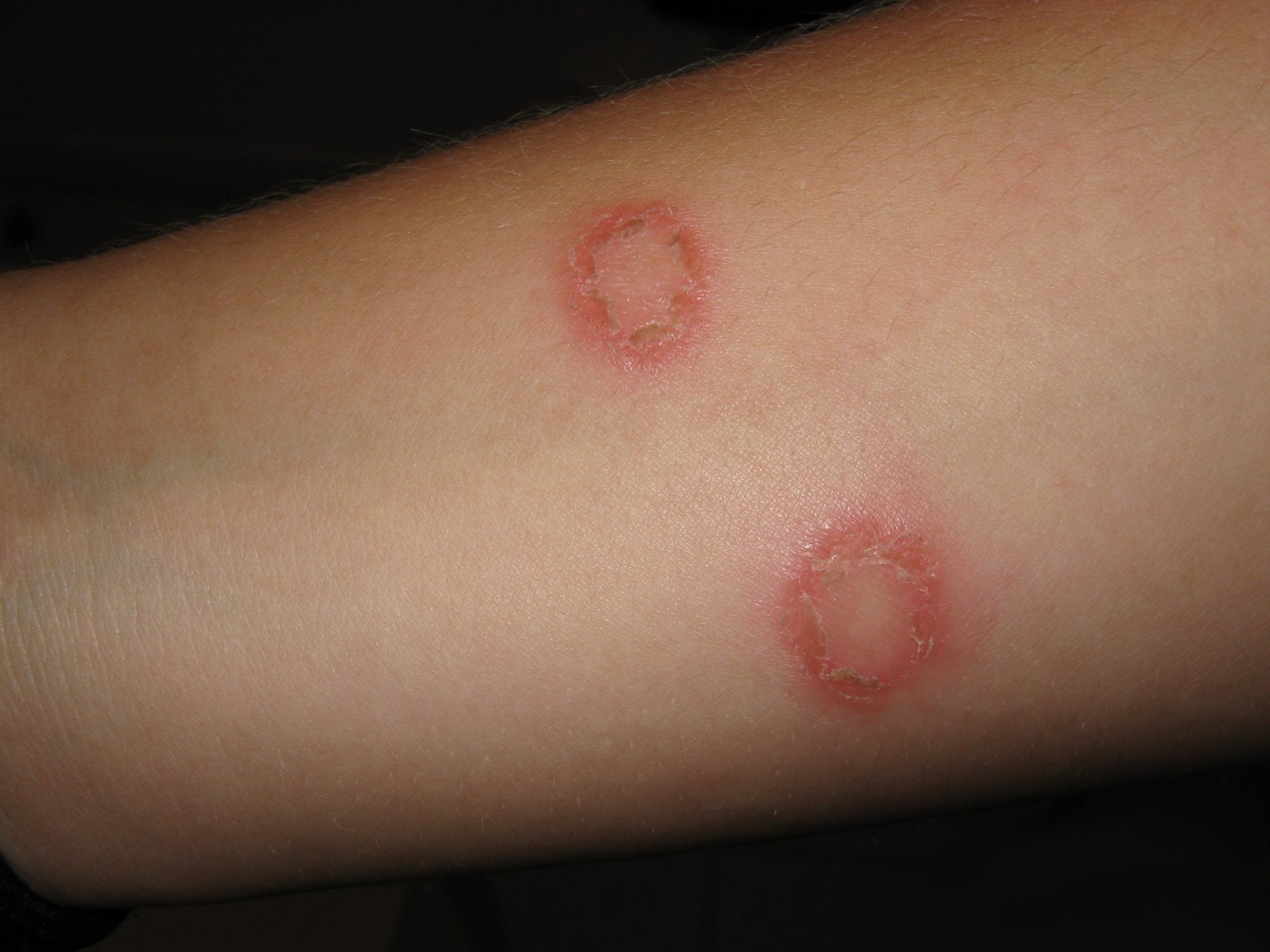 Ringworm, also known as tinea corporis, is another fungal infection. It can appear at any part of the body and can affect people at any age, but is more common among children. It can be spread by contact with an infected person or animal, contaminated clothing or furniture.
Ringworm, also known as tinea corporis, is another fungal infection. It can appear at any part of the body and can affect people at any age, but is more common among children. It can be spread by contact with an infected person or animal, contaminated clothing or furniture.
Symptoms:The ringworm looks like a circular, red sore, which in some cases has a raised structure. Sometimes it may be accompanied by scaling of the skin or rash.
Treatment: Ringwormsare usually treated by antifungal medications applied on the affected skin area. The more serious cases may require oral drugs.
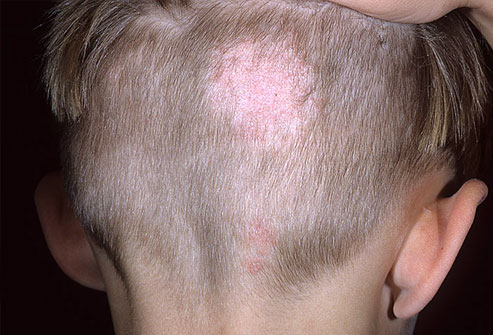 Tinea capitis is a fungal infection which targets the scalp and hair. It isspread by infected person or animal, mostly by infected hairs and contaminated objects.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection which targets the scalp and hair. It isspread by infected person or animal, mostly by infected hairs and contaminated objects.
Symptoms: Tinea capitis causes hair loss on some areas, resulting in bald spots on the head, often accompanied by a scaly rash. A more severe form of tinea capitis is called keroin – a large, oozy, painful rash. If not treated on time, it can lead to permanent hair loss.
Treatment: Unlike the previous two skin infections, the damage is done deep in the folliclewith tinea capitis, so topical treatment will not work. Medications are taken orally and the treatment usually lasts from 1 to 3 months.
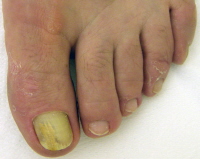 Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails. It often occurs as a result of untreated athlete’s foot or tinea manuum (which affects hands). People who have their nails manicured often are more vulnerable to this kind of infection.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails. It often occurs as a result of untreated athlete’s foot or tinea manuum (which affects hands). People who have their nails manicured often are more vulnerable to this kind of infection.
Symptoms: Redness and swelling of the affected area, the nail becomes thick and brittle and may even fall.
Treatment: The hard surface of the nail makes topical medication inefficient, so usually oral drugs are prescribed. Sometimes the removal of part or the entire infectednail may be required.
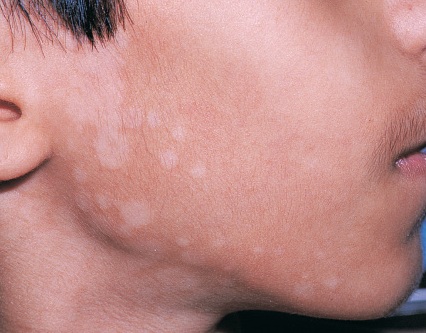 Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection damaging the outermost layer of the skin anywhere on the body. It affects primarily adolescents and adults but can be seen in children as well.
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection damaging the outermost layer of the skin anywhere on the body. It affects primarily adolescents and adults but can be seen in children as well.
Symptoms: The most obvious sign is discoloration of the affected area. Variable white, pink or brown spots may appear on the skin.
Treatment: Since the infection is on the surface of the skin, it is treated by topical antifungals. More serious cases may require oral medications.
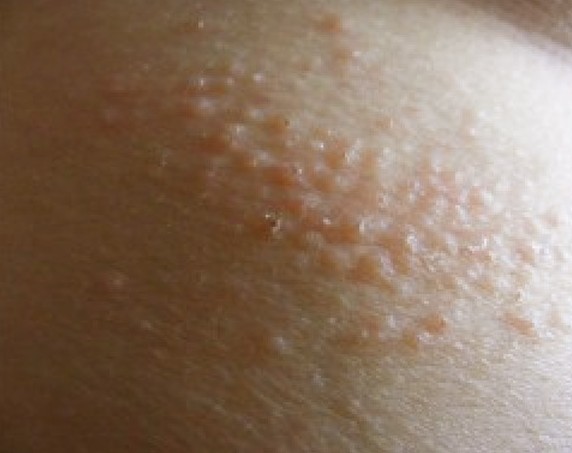
 Cutaneous Candidiasis is another fungal infection of the skin. It is usually caused by the disturbed bacteria-yeast balance in the body or a breach in its immune system. It occurs most often in moist parts of the body, such as the groins, the area under the armpits and breasts, and between the folds of obese persons.
Cutaneous Candidiasis is another fungal infection of the skin. It is usually caused by the disturbed bacteria-yeast balance in the body or a breach in its immune system. It occurs most often in moist parts of the body, such as the groins, the area under the armpits and breasts, and between the folds of obese persons.
Symptoms: Red rash, itching and moist peeling
Treatment: Cutaneous Candidiasis is most commonly treated by topical anti-fungals. In most severe cases oral medications are prescribed.
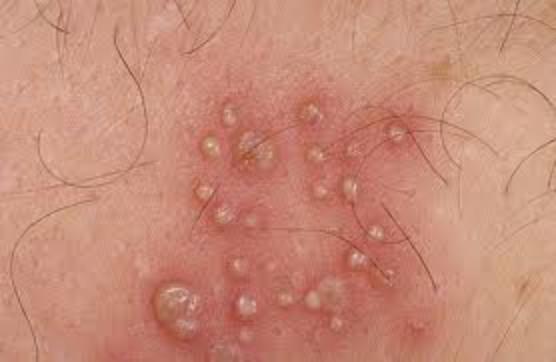 Jock itch is a fungal infection which predominantly affects the groin area of men. The reason is that this fungus thrives in moist, dark environment, such as the groins. Women are rarely affected.
Jock itch is a fungal infection which predominantly affects the groin area of men. The reason is that this fungus thrives in moist, dark environment, such as the groins. Women are rarely affected.
Symptoms: Red spots accompanied by itching and scaling on the groin, genitals, buttocks and inner thighs; festering blisters, sweating and burning sensation in the groin area.
Treatment: First you can try home treatment which involvesregular washing of the problem area with water, applying antifungal cream, changing underwear daily. If there’s no improvement, your doctor may prescribe more powerful antifungal medication.
 Valley fever, also known as Coccidioides, is a respiratory infection. It is caused by a fungus which grows in dry soil in various parts of the world. People with weakened immune system are especially vulnerable to a serious infection and are likely to develop complications.
Valley fever, also known as Coccidioides, is a respiratory infection. It is caused by a fungus which grows in dry soil in various parts of the world. People with weakened immune system are especially vulnerable to a serious infection and are likely to develop complications.
Symptoms: fever, ache in the head and muscles, pain in the joints (knees, ankles), and cough
Treatment: The optimal treatment of valley fever is still an object of research. Still, antifungals are commonly used to prevent and treat complications. Severe cases may require respiratory therapy and hospitalization.
You can find more information on fungal skin infections in the following video: