 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
A serious liver condition caused by the Hepatitis B virus is known as Hepatitis B or Hep B. It is usually seen in the people falling in the age group of 20 to 49 years. Statistics available with the CDC has shown that the number of people contracting Hepatitis B has gone down considerably from 200,000/year in the 1980s to 43,000/year in 2007.
If the condition lasts for more than 6 months, it is known as chronic Hepatitis B infection. It puts the person at risk of developing conditions like liver failure, liver cancer and cirrhosis, where there is permanent scarring of the liver. Currently there are 1.25 million people who are Hepatitis B virus carriers in the United States alone.
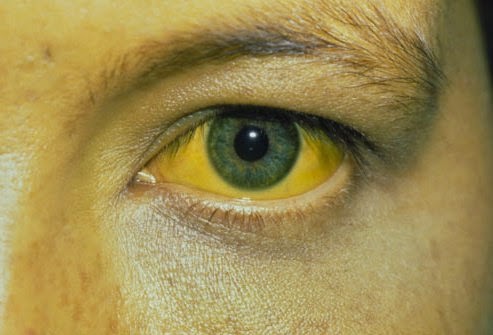 Once the Hepatitis B virus infects the body, the person may remain asymptomatic, or feel sick for a period of few days or weeks. In case the person becomes ill rapidly, it is termed as fulminant Hepatitis.
Once the Hepatitis B virus infects the body, the person may remain asymptomatic, or feel sick for a period of few days or weeks. In case the person becomes ill rapidly, it is termed as fulminant Hepatitis.
Sometimes the patient may remain asymptomatic for as long as 6 months. The initial symptoms can be as follows:
When the body fights off the infection, the symptoms can go away. However, if they persist, it is because the person has chronic Hep B. A person with chronic Hepatitis B can remain asymptomatic and need not be aware of the presence of the infection. Even in this scenario they can pass the infection to others. Such people can develop symptoms of liver failure or cirrhosis over a period of time.
The complications of Hepatitis B are:
The doctor should be contacted in case the following symptoms are noticed:
If the person seems confused or is in delirium, they should be taken to emergency care. The doctor should also be informed if one have been exposed to the virus. In case an infected person becomes pregnant or a pregnant person is exposed to the virus, they should consult the doctor immediately.
Hepatitis B is caused when the HBV passes from person to person via blood, semen or other body fluids. Its common transferring modes are:
Since Hepatitis B is transmitted via body fluids, the risk of contracting the infection increases in the following cases:
Within two weeks of exposure to Hepatitis B, you can get yourself vaccinated and also get an injection of Hepatitis immune globulin, which helps in fighting off the infection.
If the symptoms start appearing, it is important to take bed rest and not consume anything which can harm the liver. This includes alcohol, acetaminophen, herbal remedies or supplements which worsen the liver damage.
For chronic active Hepatitis B, the doctor usually prescribes aggressive treatment, if the patient is an inactive carrier, he is kept under observation.
The following medications or treatments are prescribed for people with chronic Hepatitis B:
The first thing to that can be done is to learn about Hepatitis B. Having a short note on Hepatitis B from the CDC can be helpful. Since it does not spread via casual contact, keep in touch with family and friends. Ensure that you have a healthy diet, exercise daily and get adequate sleep. Avoid substances which can harm the liver and get vaccinated and test for Hepatitis A.