 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
Blood is circulated through blood vessels by the heart to feed the organs oxygen and nutrients necessary for proper body function. If any of the blood vessels are damaged, the body repairs it through a clotting process which minimizes damage, whether it’s to an artery, a vein, or smaller capillaries, and prevents too much blood from escaping. Sometimes this mechanism is insufficient due to a large injury and internal bleeding can occur. While external bleeding is readily recognized, internal bleeding is difficult to spot.
Internal bleeding can occur in any tissue of the body, including organs and body cavities such as the abdomen, chest, and head. Internal bleeding may not be discovered for hours, depending on the extent of damage to internal blood vessels. Any symptoms may not arise until there is a significant amount of blood loss within the area. Blood leaks into a cavity or organ when a vein or artery has suffered damage. The greater the damage, the greater the amount of bleeding. Damage may be too great for the clotting mechanism to work. People who take anti-clotting agents can experience blood loss even from minor injuries.
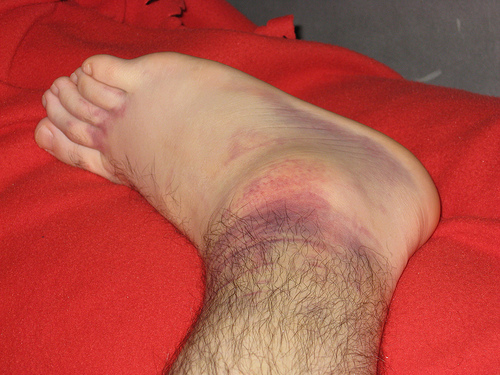 The symptoms of internal bleeding can vary depending on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the injury to the blood vessels, and the speed of blood loss. Slow bleeding can cause anemia, feeling tired, weakness, paleness, and even shortness of breath. Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract can cause vomiting with blood present, and blood in the urine or stool. Rapid bleeding can cause dizziness and shock very quickly and can lead to loss of consciousness. Other common symptoms can include abdominal pain and bruising.
The symptoms of internal bleeding can vary depending on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the injury to the blood vessels, and the speed of blood loss. Slow bleeding can cause anemia, feeling tired, weakness, paleness, and even shortness of breath. Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract can cause vomiting with blood present, and blood in the urine or stool. Rapid bleeding can cause dizziness and shock very quickly and can lead to loss of consciousness. Other common symptoms can include abdominal pain and bruising.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially if the symptoms are accompanied by any of the following conditions:
Stabilizing the patient is the most important initial treatment for internal bleeding and this includes following the ABCs of resuscitation:
Additional treatment for internal bleeding will depend on the area and source of the bleeding. The goal is to find the source and stop the bleeding and then repair the damaged blood vessel and then repair and damage caused by the bleeding. Once the immediate situation has been taken care of, treatment will consist of ways to prevent the bleeding from happening again.