 New Health Guide
New Health Guide
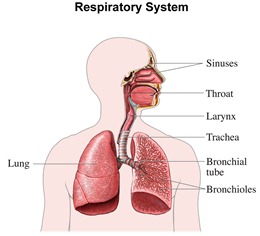 Respiratory disorders refer to the pathological conditions that disturb the function of organs and tissues that are responsible for the gas exchange in higher organisms. They usually affect alveoli, bronchi, bronchioles, trachea, pleura and pleural cavity and upper respiratory tract. Respiratory disorders can be a mild malady like asthma, or fatal diseases like lung cancer, pulmonary embolism and bacterial pneumonia. Below we look at some of the common respiratory disorders.
Respiratory disorders refer to the pathological conditions that disturb the function of organs and tissues that are responsible for the gas exchange in higher organisms. They usually affect alveoli, bronchi, bronchioles, trachea, pleura and pleural cavity and upper respiratory tract. Respiratory disorders can be a mild malady like asthma, or fatal diseases like lung cancer, pulmonary embolism and bacterial pneumonia. Below we look at some of the common respiratory disorders.
Respiratory disorders have various conditions ranging from mild to chronic. Some conditions appear mild but they affect other organs in the body (mild obstructive pulmonary disease causes heart problems). Some of the most common chronic respiratory conditions are as follows.
Asthma is caused by allergens such as mold, pollen, smoke, stern physical activities, foods like nuts and berries and animal dander. Exposure to these irritating substances cause the airways to swell and narrow the airflow passage, due to which excess mucus is produced, that further irritates the throat, triggering cough and shortness of breath.
Treatment. Although asthma is incurable, its symptoms are controllable. Medications like oral and intravenous corticosteroids, short-acting beta agonists and ipratropium (atrovent) can give quick relief to asthma patients. Long-standing medicines like long-acting beta agonists, leukotriene modifiers and inhaled corticosteroids are prescribed for severe asthma condition.
Here is a video to explain what asthma is.
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that usually occurs in children younger than the age of 2 and adults older than 65. Pneumonia agitates the air sacs in the lungs by producing phlegm that causes cough with phlegm, chills, fever, and breathing with obstruction.
Treatment. Various types of bacteria and viruses cause this infection and medications depend on the severity of the infection and age of the patient. For mild symptoms, patient might take aspirin, ibuprofen or ponstan and can also get a flu shot or vaccination to avoid getting this infection. To prevent pneumonia in little children, make sure that they have been vaccinated.
Emphysema is a respiratory infection caused by the air pollution, polluted fumes, silica dust and tobacco smoking including marijuana and weed. Emphysema usually crops up when the air sacs in the lungs are damaged, causing dreadful shortness in breath. One may have emphysema for quite a few years without feeling any signs or symptoms.
Treatment. Emphysema occurs gradually and it cannot be cured and its damage cannot be repealed. However, drugs like bronchodilators, steroids and antibiotics can delay the progression of the disease. Lung volume reduction surgery and pulmonary rehabilitation therapy also help with this disease.
Bronchitis is a common respiratory infection that inflames the lining of the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for delivering air to and from your lungs, causing disruption in the airflow. It is caused by severe cold or any other respiratory infection. This infection usually occurs in two forms, acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. The chronic form is often caused by smoking.
Treatment. Usual symptoms include cough, phlegm, fatigue with fever and chest discomfort. This infection cannot be cured by just over-the-counter drugs; you will need prescription antibiotics, cough relief medicines and inhalers. Humidifier and OTC pain relievers are highly recommended for acute bronchitis, while pulmonary rehabilitation therapy can help patients with chronic bronchitis.
Pulmonary embolism infection is caused by blood lumps that trek up to your lungs, instigating obstruction in one or more arteries. The symptoms usually include severe cough with blood-tinged sputum, sudden obstruction in breathing with awful chest pain. These symptoms can be caused by some other infection but if they persist, have them immediately checked because if it’s pulmonary embolism, it could be fatal.
Treatment. Medications like anticoagulants (anti-clotting) and thrombolytics (clot dissolvers) are used for urgent treatment (to reduce the risk of anything serious). Other measures that can help prevent blood clotting are graduated compression stockings, pneumatic compression and anticoagulant therapy.
Lung cancer, as the name suggests, is a type of cancer that corrodes the lungs. There is no easy way to tell if you have lung cancer, it is an invisible attacker and only shows symptoms when the disease has progressed. Lung cancer usually occurs in men and women who are habitual smokers, and it is the primary cause of cancer deaths. Symptoms include chronic cough with blood, nasal and chest obstruction, breath shortness, and weight loss. Lung cancer can occur in anybody but smokers usually make the victims list.
Treatment. After profound research, American physicians have found that some therapies like massage, meditation/yoga, and hypnosis might help lung cancer patients, while the medical treatments depend on the severity of the disease.
Learn more about lung cancer here.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease limits airflow in the lungs and causes shortness of breath. It is usually common among people above the age of 60. COPD cannot be fully cured even with the proper treatment.
Hay Fever. Hay fever is commonly known as allergic rhinitis, it occurs when a person is exposed to seasonal pollen. Hay fever is very common among children and adults, and is the most common respiratory condition.
Chronic Sinusitis. Chronic sinusitis is associated with the inflammation of one or more sinuses that result in sinus blockage. Normally it occurs after the swelling of the sinuses, production of excess mucus, or septum deviation causes drainage obstruction.
Cystic Fibrosis. Patient’s gland produces thick and sticking mucus that affects the lungs and other vital organs. CF is considered a hereditary disease and is perilous if not treated immediately. CF often leads to several chest infections, nasal obstruction, and bronchiectasis.
Pulmonary Fibrosis. Pulmonary fibrosis is associated mutilation of the lungs. It causes scarring of the lungs and affects the oxygen transfer into the blood. Pulmonary fibrosis is considered idiopathic because of its unknown nature.
Bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis is linked with deviant and irrevocable expansion of the air passages in the lungs. It is usually caused by chronic COPD, cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis, measles and short antibody level. People with this condition usually suffer from several infections due mucus in the air passages.
Occupational Lung Diseases. Occupational lung diseases occur in individuals who work around harmful fumes like coal, dust, and silica. This causes scarring of the lungs (pneumoconiosis).
Sleep Apnea. Sleep Apnea is respiratory condition that usually obstructs breathing in sleep. It causes nasal obstruction, reducing the airflow, which disturbs patient’s sleep.